Services /
Six Sigma /Implementation RolesOne key innovation of Six Sigma involves the "professionalizing" of quality management functions. Prior to Six Sigma, quality management in practice was largely relegated to the production floor and to statisticians in a separate quality department. Formal Six Sigma programs borrow martial arts ranking terminology to define a hierarchy (and career path) that cuts across all business functions.
Six Sigma identifies several key roles for its successful implementation.
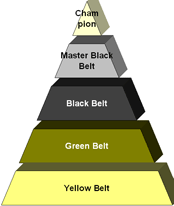
- Executive Leadership includes the CEO and other members of top management. They are responsible for setting up a vision for Six Sigma implementation. They also empower the other role holders with the freedom and resources to explore new ideas for breakthrough improvements.
- Champions take responsibility for Six Sigma implementation across the organization in an integrated manner. The Executive Leadership draws them from upper management. Champions also act as mentors to Black Belts.
- Master Black Belts, identified by champions, act as in-house coaches on Six Sigma. They devote 100% of their time to Six Sigma. They assist champions and guide Black Belts and Green Belts. Apart from statistical tasks, they spend their time on ensuring consistent application of Six Sigma across various functions and departments.
- Black Belts operate under Master Black Belts to apply Six Sigma methodology to specific projects. They devote 100% of their time to Six Sigma. They primarily focus on Six Sigma project execution, whereas Champions and Master Black Belts focus on identifying projects/functions for Six Sigma.
- Green Belts, the employees who take up Six Sigma implementation along with their other job responsibilities, operate under the guidance of Black Belts.
- Yellow Belts, trained in the basic application of Six Sigma management tools, work with the Black Belt throughout the project stages and are often the closest to the work.